- Heat Exchange Coils
- Dispensing
- Brewing
- Tubing
- Fittings & Clamps
-
Recently Viewed
You have no recently viewed items.

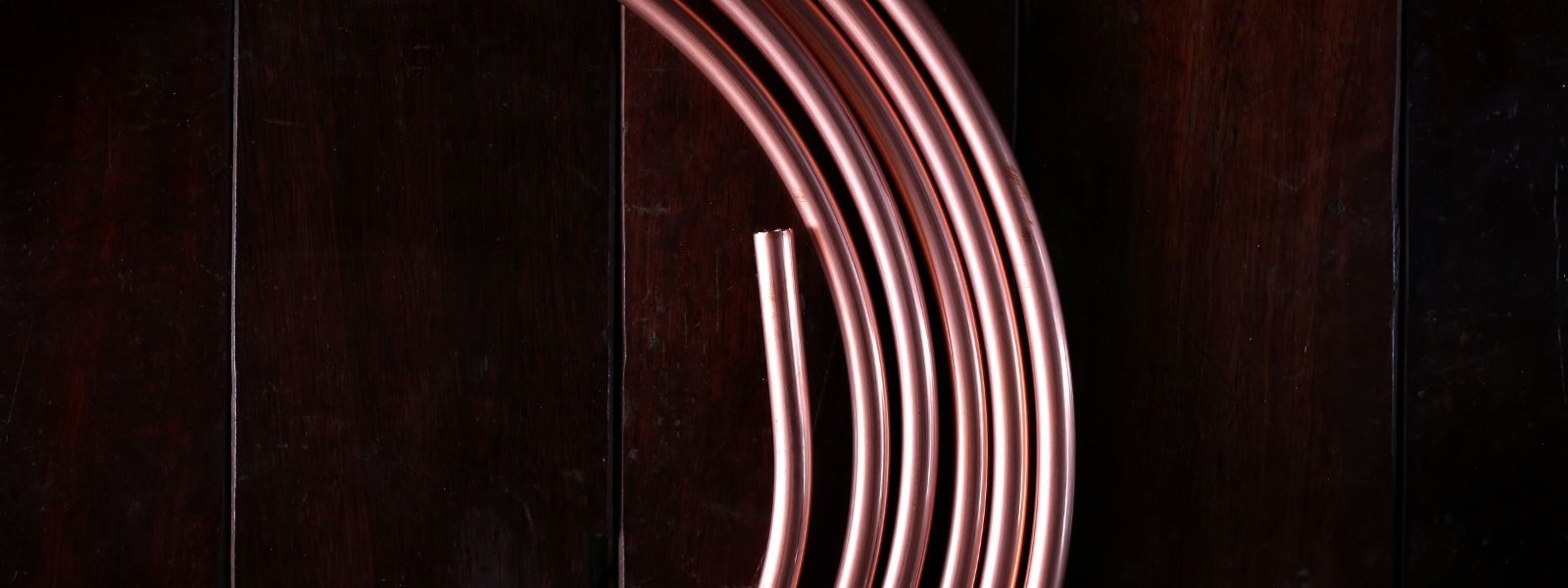
Copper Refrigeration Tubing: The Backbone of Cooling Systems
Copper Refrigeration tubing is a critical component in any cooling system, whether it's your NY Brew Supply Wort Chiller, in your kitchen refrigerator, an air conditioning unit, or large-scale commercial refrigeration setups. This tubing plays a vital role in the transfer of refrigerants, enabling the heat exchange process that keeps your spaces cool and your perishables fresh. Understanding the importance, material choices, and measurement techniques for refrigeration tubing is essential for anyone involved in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) or refrigeration industries.
The Role of Refrigeration Tubing
Refrigeration tubing is designed to carry refrigerants through the cooling system. The tubing connects various components, such as the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve. As the refrigerant travels through the tubing, it absorbs heat from the environment and then releases it elsewhere, effectively cooling the desired area. The efficiency of this process depends heavily on the quality and design of the tubing.
Material Choices: Copper and Beyond
Traditionally, copper has been the material of choice for refrigeration tubing due to its excellent thermal conductivity, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion. Copper tubing is easy to shape, which allows for custom installations in tight spaces. Its ability to withstand high pressures makes it ideal for use in both residential and commercial refrigeration systems.
However, other materials like aluminum and stainless steel are also used in specific applications. Aluminum is lighter and less expensive than copper, making it suitable for larger installations where weight and cost are significant factors. Stainless steel, while more costly, offers superior strength and durability, particularly in harsh environments where corrosion resistance is crucial.
Measuring Refrigeration Tubing
Accurate measurement of refrigeration tubing is essential for ensuring the system's efficiency and proper operation. Tubing is typically measured by its outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness, which together determine the internal diameter (ID) of the tube. The ID is crucial as it influences the flow rate of the refrigerant through the system.
1. Outside Diameter (OD): The OD is the total width of the tubing, measured from one outer edge to the opposite outer edge. This measurement is critical because it affects how the tubing fits with connectors, valves, and other components in the refrigeration system.
2. Wall Thickness: The wall thickness refers to the distance between the outer surface and the inner surface of the tubing. This measurement is important because it influences the tubing's ability to withstand pressure. Thicker walls can handle higher pressures but may also reduce the internal flow capacity of the tubing.
3. Inside Diameter (ID): The ID is calculated by subtracting twice the wall thickness from the OD. The ID determines how much refrigerant can flow through the tubing at any given time, which impacts the overall performance of the cooling system.
It's important to note that refrigeration tubing sizes are often specified in inches or millimeters, depending on the region and the specific application. For example, in North America, refrigeration tubing is usually measured in inches, while in Europe, millimeters are more common.
Choosing the Right Size
Selecting the right size of refrigeration tubing is crucial for the system’s efficiency and longevity. If the tubing is too narrow, it can restrict refrigerant flow, leading to reduced cooling performance and increased pressure on the system components. Conversely, tubing that is too large can result in an inefficient system with higher energy consumption.
When determining the appropriate tubing size, professionals consider factors such as the type of refrigerant, the length of the tubing run, and the cooling capacity required. Calculations often involve the use of charts and formulas that take into account these variables to ensure optimal system performance.
Conclusion
Refrigeration tubing is more than just a conduit for refrigerants; it's a vital part of the cooling system's infrastructure. Whether made from copper, aluminum, or stainless steel, the right tubing ensures that the system operates efficiently and reliably. Proper measurement of refrigeration tubing—considering the outside diameter, wall thickness, and inside diameter—is key to achieving the desired performance and longevity of the system. By understanding these fundamentals, HVAC professionals can make informed decisions that contribute to the effectiveness and sustainability of refrigeration systems.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.